
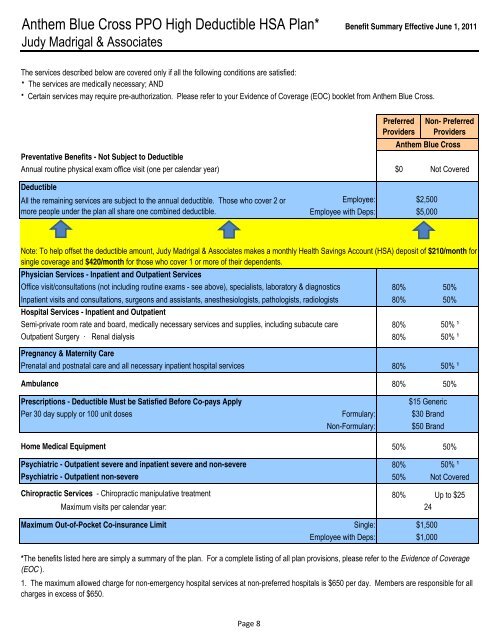

With a PPO plan, you would be responsible for paying your co-pays, coinsurance, and deductible until you reach your out-of-pocket maximum. PPO plans typically have larger networks than HDHPs and other types of healthcare plans, and they do provide some out-of-network services for medically necessary healthcare. PPO plans usually charge a higher monthly premium and offer lower deductibles. The deductible must be at least $1,500 for an individual plan or $3,000 for a family plan (not including out-of-pocket costs from seeking care out-of-network).Ī PPO, or Preferred Provider Organization, is a health plan including a group of providers contracted with your insurance plan for a lower price.Total out-of-pocket cost cannot exceed $7,500 for an individual plan or $15,000 for a family plan (not including out-of-pocket costs from seeking care out-of-network).To be considered an HDHP, the plan must adhere to the following guidelines set by the IRS: Once the deductible is met, you are only responsible for co-pays and coinsurance for medically necessary in-network health care. All health costs, other than certain types of preventive care, must go toward the deductible first.įor example, if you visit with a specialty GI doctor, you would have to pay for the visit out-of-pocket, which would go toward your annual deductible. HDHPs offer a lower monthly premium but a higher deductible. HSA funds can be used as a tax-advantaged way to pay for healthcare costs in retirement, including Medicare premiums.Ī High Deductible Health Plan is sometimes abbreviated as HDHP.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
